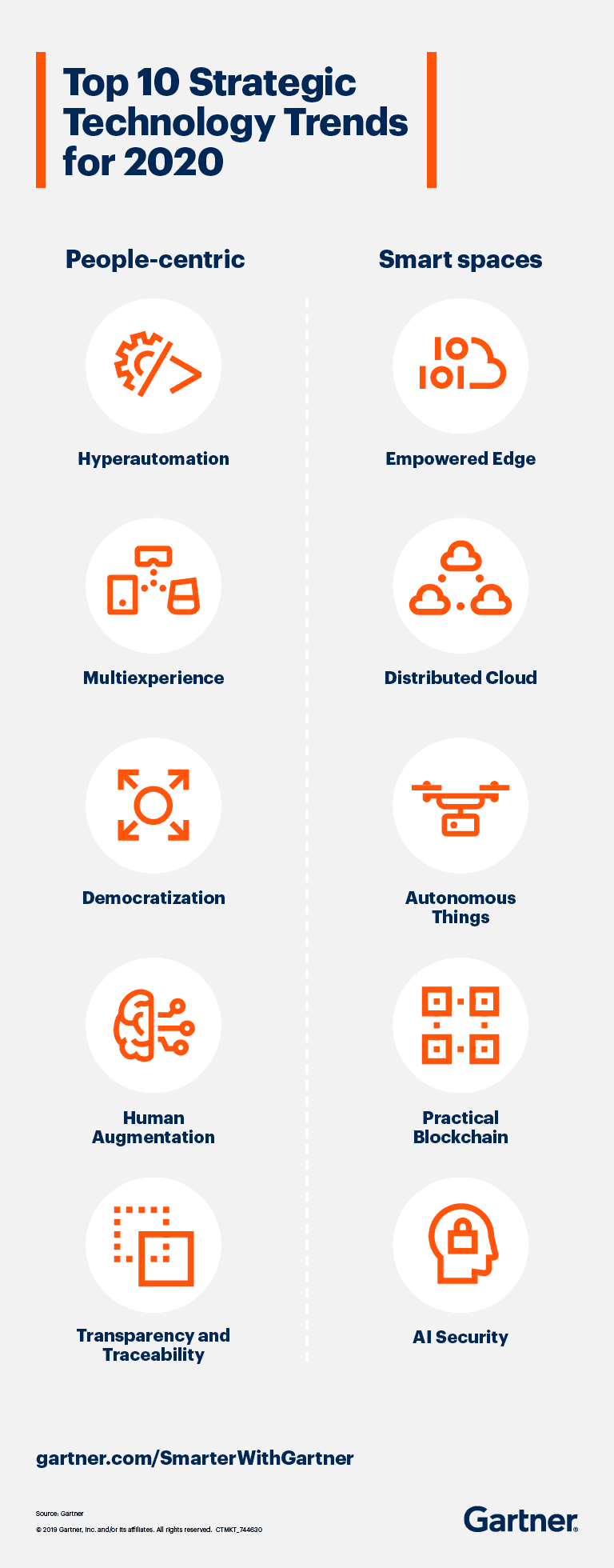
Hyperautomation, blockchain, AI security, distributed cloud and autonomous things drive disruption and create opportunities in this year’s strategic technology trends.
Human augmentation conjures up visions of futuristic cyborgs, but humans have been augmenting parts of the body for hundreds of years. Glasses, hearing aids and prosthetics evolved into cochlear implants and wearables. Even laser eye surgery has become commonplace.
But what if scientists could augment the brain to increase memory storage, or implant a chip to decode neural patterns? What if exoskeletons became a standard uniform for autoworkers, enabling them to lift superhuman weights? What if doctors could implant sensors to track how drugs travel inside a body?
Technology is now on the cusp of moving beyond augmentation that replaces a human capability and into augmentation that creates superhuman capabilities.
Want to publish your own articles on DistilINFO Publications?
Send us an email, we will get in touch with you.
How these changes will impact the world and business makes human augmentation one of Gartner’s top 10 strategic technology trends that will drive significant disruption and opportunity over the next five to 10 years.
The trends are structured around the idea of “people-centric smart spaces,” which means considering how these technologies will affect people (i.e., customers, employees) and the places that they live in (i.e., home, office, car).
“These trends have a profound impact on the people and the spaces they inhabit,” said Brian Burke, Gartner Research VP, at Gartner 2019 IT Symposium/Xpo™ in Orlando, Florida. “Rather than building a technology stack and then exploring the potential applications, organizations must consider the business and human context first.”
These trends don’t exist in isolation; IT leaders must decide what combination of the trends will drive the most innovation and strategy.
For example, artificial intelligence (AI) in the form of machine learning (ML) with hyperautomation and edge computing can be combined to enable highly integrated smart buildings and city spaces. In turn, these technology combinations enable further democratization of the technology.
Trend No 1. Hyperautomation
Automation uses technology to automate tasks that once required humans.
Hyperautomation deals with the application of advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), to increasingly automate processes and augment humans. Hyperautomation extends across a range of tools that can be automated, but also refers to the sophistication of the automation (i.e., discover, analyze, design, automate, measure, monitor, reassess.)
Hyperautomation often results in the creation of a digital twin of the organization
As no single tool can replace humans, hyperautomation today involves a combination of tools, including robotic process automation (RPA), intelligent business management software (iBPMS) and AI, with a goal of increasingly AI-driven decision making.
Although not the main goal, hyperautomation often results in the creation of a digital twin of the organization (DTO), allowing organizations to visualize how functions, processes and key performance indicators interact to drive value. The DTO then becomes an integral part of the hyperautomation process, providing real-time, continuous intelligence about the organization and driving significant business opportunities.
Trend No. 2: Multiexperience
Multiexperience replaces technology-literate people with people-literate technology. In this trend, the traditional idea of a computer evolves from a single point of interaction to include multisensory and multitouchpoint interfaces like wearables and advanced computer sensors.
For example, Domino’s Pizza created an experience beyond app-based ordering that includes autonomous vehicles, a pizza tracker and smart speaker communications.
In the future, this trend will become what’s called an ambient experience, but currently multiexperience focuses on immersive experiences that use augmented reality (AR), virtual (VR), mixed reality, multichannel human-machine interfaces and sensing technologies. The combination of these technologies can be used for a simple AR overlay or a fully immersive VR experience.
Source: Gartner







